You may have heard about this orthopedic issue that can cause pain, an awkward gait, or difficulties in running. You may be wondering if your child is showing symptoms of tibial torsion, and you want to learn more. In this article, you will understand tibial torsion, its causes and symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and the possible treatments.
Definition of Tibial Torsion
Tibial torsion is a common orthopedic problem in children. It occurs when the tibia bone is not correctly aligned with the thigh bone. Usually, these bones are aligned straight when the child is standing. However, when the tibia bone is rotated inward or outward, it can result in tibial torsion.
Different Causes of Tibial Torsion
Genetic Factor
One of the main factors of tibial torsion in children is genetics, which can predispose the child to have misaligned leg bones. This can be due to a variation in bone structure that can be passed down from generation to generation.
Intrauterine Malpositioning
Intrauterine malpositioning can also cause tibial torsion in children. For example, if the baby is positioned asymmetrically in the mother’s womb or if the fetus’s leg is wrapped around the other leg, it can affect the formation of the leg bones.
Trauma
Trauma, including leg injuries, can disrupt bone growth. Leg fractures, especially those affecting the growth plate, can also result in changes in bone alignment.
Abnormal Bone Development
A leg length discrepancy or abnormal curvature of the tibia bone can affect its alignment with the femur. Abnormalities in bone growth can also cause tibial torsion in children.
No Apparent Reason
Sometimes, tibial torsion can be idiopathic, meaning no apparent cause exists. Doctors may then monitor the child’s growth and observe the torsion’s progression.
Symptoms of Tibial Torsion
The symptoms of tibial torsion can vary from one child to another, depending on the severity of the condition. Children with mild tibial torsion may not have any signs or may only experience mild symptoms that do not hinder their normal daily activities. The manifestations can be more pronounced and potentially painful for children with more severe torsion.
Awkward Gait
This is the most common symptom of tibial torsion in children. They may have difficulty walking normally, with their feet turned outward or inward. In severe cases, they may struggle to run, jump, or engage in other physical activities. Some children may even trip or fall frequently.
Knee and Ankle Pain
Children may experience pain or stiffness in the knees or ankles, especially after exercising. The pain may be more pronounced on the side of the more twisted leg.
Diagnosis of Tibial Torsion
Diagnosis by a Healthcare Professional
The diagnosis of tibial torsion typically begins with a thorough physical examination conducted by a specialist in pediatric orthopedics. The doctor will carefully examine the child’s gait and observe for signs of inward or outward foot rotation. Leg rotation tests may be performed to assess the range of motion and resistance to rotation. The EVO Laboratory performs diagnostics, so you should schedule an appointment now.
Diagnosis through X-rays
X-rays may also be conducted to confirm the diagnosis of tibial torsion. The X-ray can measure the angle of tibial torsion relative to the femur and determine the degree of rotation. The images can also help rule out other orthopedic problems that may cause similar symptoms.
Other Diagnostic Methods
In some cases, a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to provide a more detailed evaluation of the tibia and femur and detect other bone or joint abnormalities. However, these tests are generally not necessary to diagnose tibial torsion.
Different Treatments for Tibial Torsion
Good news! Tibial torsion is a condition that can be treated, and here are the various treatment options available to address the situation.
Monitoring the Condition’s Progression
Sometimes, tibial torsion may resolve independently over time without requiring active treatment. Doctors may recommend simple monitoring of the torsion, especially in young children whose bones are still developing.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen the ankle and foot muscles, improve mobility, and correct gait issues. Physical therapy exercises can help support the ankle and foot muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
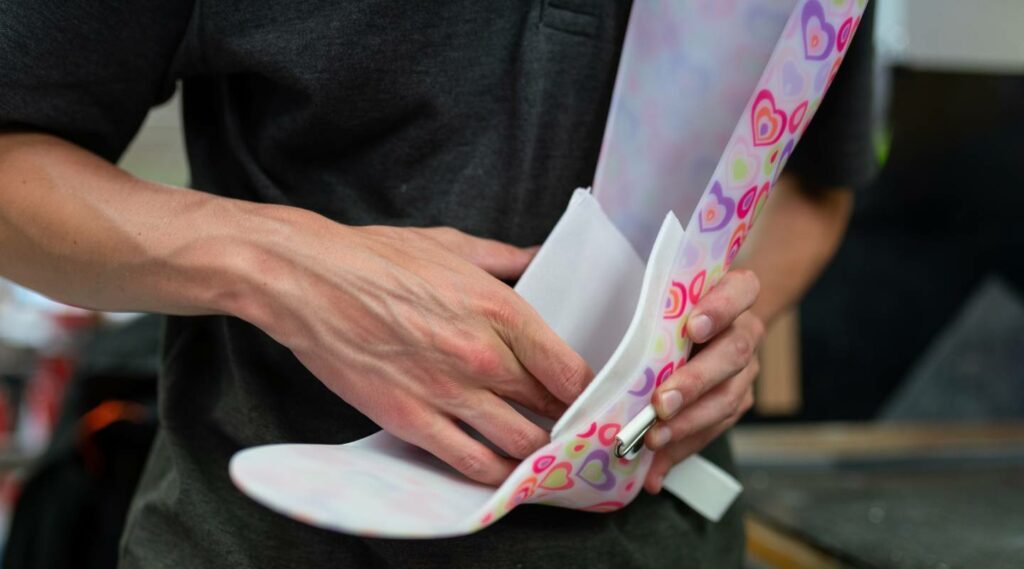
Use of Ankle-Foot Orthoses (AFO)
Ankle-foot orthoses wrap around the ankle and foot to provide additional support. They can correct foot positioning, maintain stability, and alleviate pain. Ankle-foot orthoses are generally recommended for children with moderate to severe tibial torsion. The EVO Laboratory specializes in creating orthoses, and we would be happy to assist your child in their treatment!

Surgical Intervention
In the most severe cases of tibial torsion, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the position of the bones and joints. However, surgery is typically considered a last-resort treatment option and is only recommended if other treatment options have failed.
Tibial Torsion in Children: Key Takeaways
- Tibial torsion in children is a relatively common condition that can affect gait and cause pain;
- Treatment depends on the severity of the torsion and the symptoms presented: in some cases, monitoring or physiotherapy may be sufficient, while in others, orthoses or surgical intervention may be necessary;
- It is essential to consult a doctor if you suspect your child has tibial torsion to determine the best treatment plan for them;
- With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most children with tibial torsion can fully recover and continue to lead an active and healthy life;
- As orthopedic specialists, the EVO Laboratory is here to answer all your questions and help you find the best solutions for your child. Schedule an appointment now!